Table of Contents
What is phishing?
Traditional login methods that use just a username and password are largely a thing of the past. By now, most end users are familiar with multi-factor authentication (MFA), which uses at least one second factor (if not more) to verify user identity. According to recent studies, 87% of employees use MFA, partly because 95% of companies now require it.
However, MFA is not a one-size-fits-all solution to privacy and security in authentication. Phishing attacks, with their ever-evolving sophistication, continue to prey on unsuspecting individuals, leaving a trail of compromised accounts and stolen information in their wake.
Phishing-resistant MFA is an innovative approach that promises to reshape the security landscape. In this blog, we’ll cover phishing-resistant MFA and highlight why it should be an integral part of your security strategy.
But before we start, let’s quickly remind ourselves what phishing and MFA are.
What is phishing?
Phishing is a form of social engineering where cybercriminals attempt to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information, such as login credentials or credit card details. These attacks typically involve fraudulent emails, text messages, or websites that appear legitimate but are designed to deceive unsuspecting users. Victims may unknowingly compromise their security by clicking on malicious links, downloading malware, or entering their credentials into fake login pages.
While MFA is designed to reduce the likelihood and impact of broken authentication, it is not foolproof against phishing. MFA fatigue can make users (and apps) susceptible to man-in-the-middle (MITM) and other attacks, leading to MFA bypass. This is why phishing-resistant MFA is crucial.
What is MFA?
Traditional MFA typically combines two or more factors from these categories:
Knowledge factor, or something you know: A password or PIN.
Possession factor, or something you have: A one-time password (OTP) generated by a mobile app or sent via SMS.
Inherence factor, or something you are: Biometrics like a fingerprint or facial recognition.
While traditional MFA significantly improves security over password-based authentication, it still has its vulnerabilities. For example, attackers can use phishing tactics to trick users into revealing OTPs (a commonly used auth factor) or passwords. And once they get this information, they can access the account.
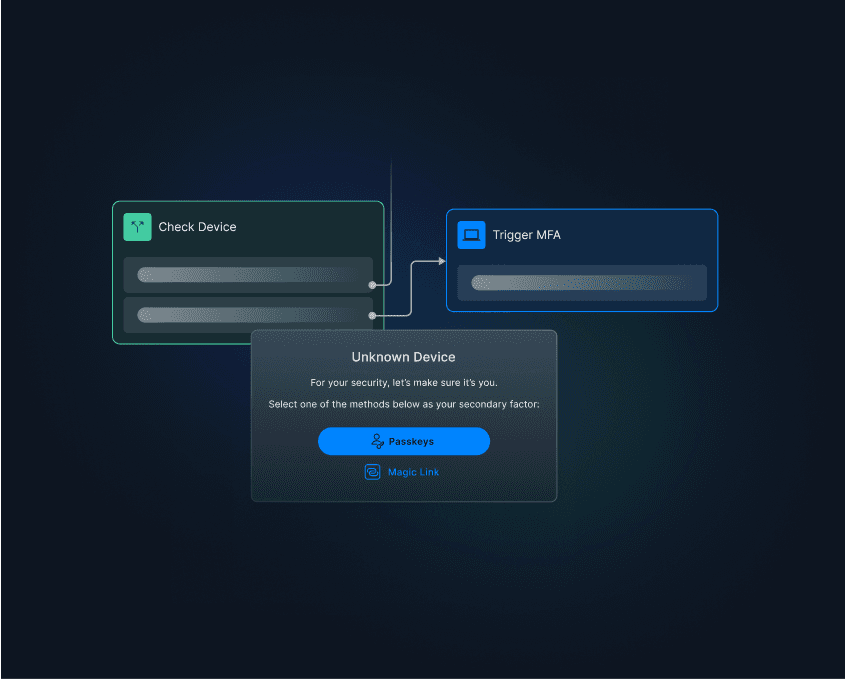
For example, an enterprise organization was being targeted by the below SMS OTP bypass attack before adding magic link MFA with Descope.
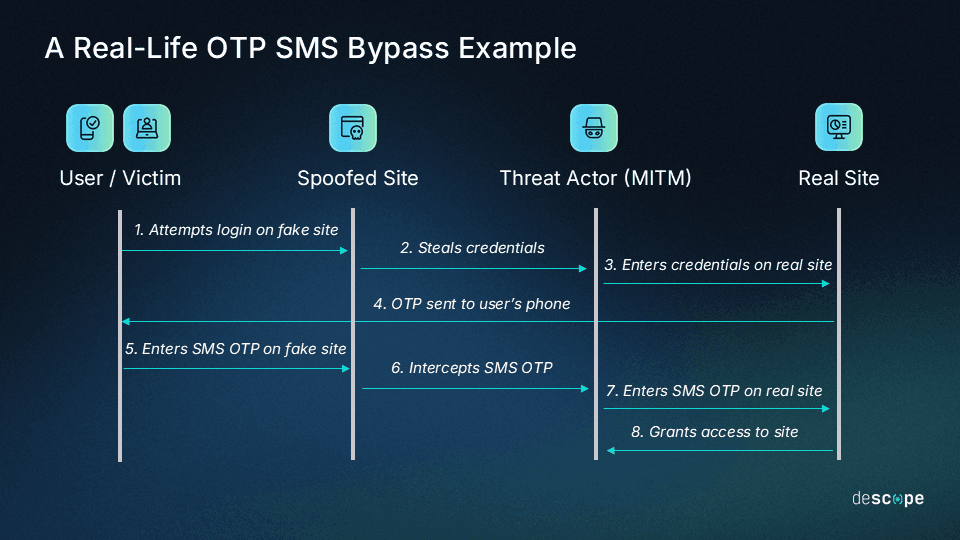
Learn more about this attack and strong MFA tips
What is phishing-resistant MFA?
Phishing-resistant MFA is a more intentional, proactive approach than traditional MFA that accounts for its vulnerabilities, incorporating proactive safeguards to counter sophisticated attacks that exploit human error. Through strong authentication, risk-based analysis and other mechanisms, phishing-resistant MFA can successfully prevent MFA bypass attempts.
Phish-resistant MFA components
Here's a look at some of the characteristics and methods commonly used in phishing-resistant MFA flows:
Strong authentication factors
Phishing-resistant MFA prioritizes factors that are difficult for attackers to steal or replicate. Traditional methods like SMS authentication and push notifications are prone to interception or spoofing, making them less secure. Instead, phish-resistant MFA relies on factors such as:
Hardware tokens: Physical devices, like FIDO2 security keys, that generate cryptographic keys.
Biometric authentication: Unique biological characteristics, such as fingerprints or facial recognition.
Certificate-based authentication: Smart cards or client certificates stored securely on a device.
These methods ensure the authentication process remains resilient against phishing attempts, even if credentials are exposed.
Risk-based authentication
Not all login attempts carry the same level of risk. Risk-based (a.k.a. adaptive) MFA analyzes contextual inputs, such as:
Login parameters: Frequency, location, and timing of login attempts.
Device posture: Checks for updates, anti-virus presence, and security configurations.
Session patterns: Identifying anomalies compared to typical user activity.
Device fingerprinting: Snapshots of a device’s installed apps, operating system, and browser.
If risk signals are detected—such as an unfamiliar device or unusual login location—the system dynamically prompts for additional authentication steps, reducing reliance on static credentials.
Behavioral analysis
MFA systems with behavioral analysis add another layer of security by continuously monitoring for non-human interactions. Indicators such as typing speed, mouse movement, or even navigation patterns can highlight bot-like behavior. If these patterns deviate significantly from human behavior, the system triggers above-mentioned adaptive measures, requiring extra authentication or locking out the account until successful verification.
This proactive approach helps identify compromised sessions in real time.
Encryption and secure communication
Authentication flows must prioritize data integrity and confidentiality. Secure MFA relies on:
End-to-end encryption: Ensures credentials and tokens are transmitted securely between devices and authentication servers.
Mutual TLS (Transport Layer Security): Verifies the identity of both the client and server during communication.
Protocol hardening: Using modern, secure protocols such as OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect with PKCE (Proof Key for Code Exchange).
By encrypting every step of the authentication process, phishing-resistant MFA prevents attackers from exploiting intercepted data.
Continuous monitoring and incident response
Phishing-resistant MFA isn’t a one-and-done solution—it’s part of a broader security ecosystem. That’s why the safest MFA systems constantly:
Analyze authentication logs: Spot unusual patterns, such as failed attempts from a specific region or rapid credential stuffing.
Integrate with SIEM tools: Feed data into Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions to improve threat intelligence.
Automate incident response: Trigger alerts or isolate suspicious accounts automatically during suspected attacks.
This helps with rapid response to potential threats, minimizing the impact of breaches.
Additional fortifications
Passwordless authentication: Moving beyond traditional passwords to methods like passkeys or token-based systems removes one of the most commonly exploited vulnerabilities.
Anti-phishing safeguards: Developers can incorporate URL validation and link filtering into MFA workflows to make sure users are interacting with genuine login pages.
User education: Even the best MFA solutions are only as effective as their users. Providing training on identifying phishing attempts and avoiding common pitfalls strengthens the human element of cybersecurity.
Backup mechanisms: While providing secure MFA recovery options, such as biometric resets, ensure fallback processes don't introduce vulnerabilities.
How to implement phishing-resistant MFA
The first step in implementing phishing-resistant MFA should be identifying the resources you need to protect.
For developers, this means thinking critically about the kinds of data and systems your app, website, or program will come into contact with.
For technology leaders, this often means checking your MFA protocols against applicable compliance requirements.
Then, you’ll need to identify the likely avenues of phishing attacks and strategize ways to reduce their susceptibility. Once you have intelligence on what and whom to protect, you’ll need to develop protections and build them into or around your MFA system. Or, you could use pre-configured phishing-resistant protocols that use public key cryptography for secure, passwordless authentication.
FIDO / WebAuthn
The Fast IDentity Online (FIDO) Alliance oversees two widely used auth standards allowing for phishing-resistant MFA without using passwords. This is important because passwords and passphrases, no matter how strong, are among the weakest factors any auth system can use.
The FIDO2 standard allows users to log in to an app or program through hardware known as a FIDO authenticator. This authenticator can either be an external security key or a compatible device such as a smartphone or laptop. A registered device creates a keypair between a server and the hardware in question, which enables authentication.
FIDO2 has two critical parts: the Web Authentication API (WebAuthn) and the Client to Authenticator Protocol (CTAP). They enable authentication through possession/inherence factors and roaming authenticators, respectively.
FIDO2 and WebAuthn are ubiquitous, with supporting 95% of user devices. They’re effective at preventing phishing attacks by taking knowledge-based credentials out of the equation altogether.
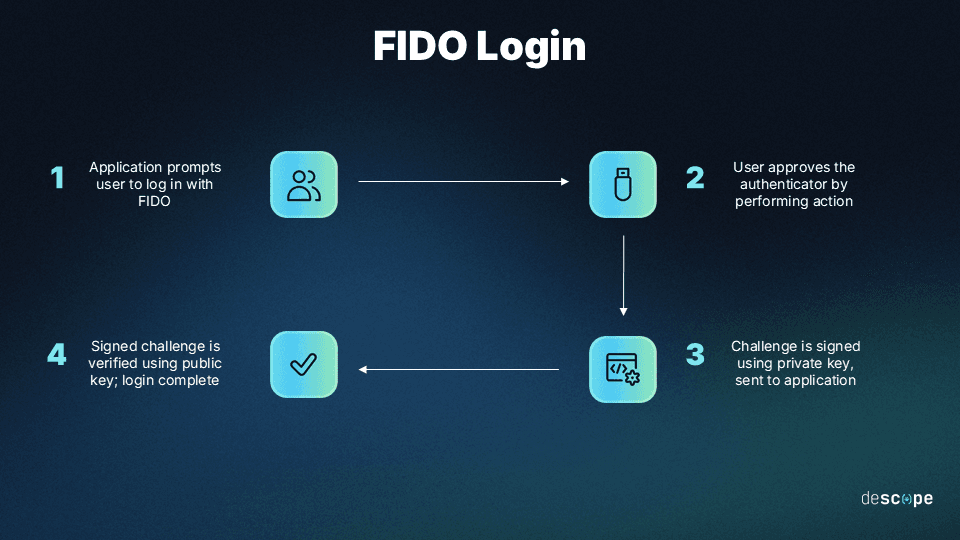
FIDO2 has two critical parts: the Web Authentication API (WebAuthn) and the Client to Authenticator Protocol (CTAP). They enable authentication through possession/inherence factors and roaming authenticators, respectively.
FIDO2 and WebAuthn are ubiquitous, with supporting 95% of user devices. They’re effective at preventing phishing attacks by taking knowledge-based credentials out of the equation altogether.
PKI-based MFA
Although niche and targeted, one option for developers is MFA based on public key infrastructure (PKI). PKI mobilizes various software, hardware, and policies to create, manage, and use public keys to authenticate users’ identities.
PKI is complex and multifaceted, but the most critical components are:
Certificates, which grant access when a public-private keypair is validated
Certificate authorities (CA), which publish public keys used to authenticate users
Registration authorities (RA), who verify user identities (and may be the same as the CA)
You can apply variations of this method to all stages of your authentication process. Common examples include PKI-encrypted smart cards containing a user’s credentials that are held up to a physical scanner (typically in conjunction with one or more other factors, such as a PIN) to provide access.
Phishing-prone authentication methods to avoid
When selecting an auth method for your app, website, or program, it’s important to know that some are inherently more vulnerable to phishing. Here are some of the approaches you should avoid for that reason:
(Just) passwords: Password-based authentication is the most conventional and insecure auth method, especially when used on its own. It relies on a user memorizing and safeguarding a unique string of characters. Without additional factors required, a successful phishing attempt will immediately break authentication.
One-time password (OTP): OTP systems generate a password that a user can only use once, which prevents later unauthorized logins when a username-password pair is compromised. However, they remain vulnerable to phishing and interception through SIM swapping and MITM attacks.
Push notifications: This approach sends users a message to a second device or account, typically prompting an input to approve the access request. However, attackers can replicate these scripts, redirecting users and obtaining access to their accounts. Push notifications can also be a vector for MFA fatigue or prompt bombing attacks, with adversaries sending repeated notifications to victims’ devices in an effort to bypass MFA.
Benefits of phishing-resistant MFA
In 2024, global phishing attacks increased by 34% compared to the previous year. So simply put, phishing isn’t going anywhere—and the most dangerous threats are growing fastest.
As cybercriminals become more adept at bypassing traditional defenses, organizations need to stay ahead. Phishing-resistant MFA reduces risk by addressing vulnerabilities in human behavior and legacy systems. While implementing these solutions may require more upfront investment, the long-term benefits in terms of security and peace of mind are invaluable.
For developers and organizations looking to secure their systems, adopting phishing-resistant MFA:
Reduces the attack surface of your auth system, removing easy targets like weak authentication factors.
Monitors for and adjusts according to patterns in your users’ behavior, removing attack vectors that cybercriminals could take advantage of.
Creates resilience with encryption by rendering stolen or leaked credentials unreadable.
Get phishing-resistant MFA with Descope
Phishing-resistant MFA is no longer a luxury but a necessity. By adopting advanced authentication methods, you can protect your organization from evolving threats and keep your data secure. Don’t wait for a breach to act—invest in phishing-resistant MFA today.
Descope helps developers easily add phishing-resistant MFA to their applications with a few lines of code. With support for strong authentication factors like passkeys and magic links, risk-based authentication and secure session management, Descope enables secure MFA without increasing friction for legitimate users.
Sign up for a Free Forever account on Descope and build your phish-resistant MFA flows with minimal coding. Have questions about our platform? Book time with our auth experts.